Alfréd Rényi
| Alfréd Rényi | |
|---|---|
| Born | 20 March 1921 Budapest, Hungary |
| Died | 1 February 1970 (aged 48) Budapest, Hungary |
| Nationality | Hungarian |
| Fields | Mathematics |
| Institutions | Eötvös Loránd University |
| Alma mater | University of Szeged |
| Doctoral advisor | Frigyes Riesz[1] |
| Doctoral students | Imre Csiszár Bonifac Donat Gyula O. H. Katona János Komlós András Prékopa Gábor Székely |
Alfréd Rényi (20 March 1921 – 1 February 1970) was a Hungarian mathematician who made contributions in combinatorics, graph theory, number theory but mostly in probability theory.[2][3]
Contents |
Life
Rényi was born in Budapest to Artur Rényi and Barbara Alexander; his father was a mechanical engineer while his mother was the daughter of a philosopher and literary critic, Bernát Alexander. He was prevented from enrolling in university in 1939 due to the anti-Jewish laws then in force, but enrolled at the University of Budapest in 1940 and finished his studies in 1944. At this point he was drafted to forced labour service, escaped, and completed his Ph.D. in 1947 at the University of Szeged, under the advisement of Frigyes Riesz. He married Katalin Schulhof (who used Kató Rényi as her married name), herself a mathematician, in 1946; their daughter Zsuzsanna was born in 1948. After a brief assistant professorship at Budapest, he was appointed Professor Extraordinary at the University of Debrecen in 1949. In 1950, he founded the Mathematics Research Institute of the Hungarian Academy of Sciences, now bearing his name, and directed it until his early death. He also headed the Department of Probability and Mathematical Statistics of the Eötvös Loránd University, from 1952. He was elected a corresponding member(1949), full member (1956) of the Hungarian Academy of Sciences
Work
He proved, using the large sieve, that there is a number 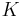 such that every even number is the sum of a prime number and a number that can be written as the product of at most
such that every even number is the sum of a prime number and a number that can be written as the product of at most 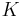 primes. See also Goldbach conjecture.
primes. See also Goldbach conjecture.
In information theory, he introduced the spectrum of Rényi entropies of order α, giving an important generalisation of the Shannon entropy and the Kullback-Leibler divergence. The Rényi entropies give a spectrum of useful diversity indices, and lead to a spectrum of fractal dimensions. The Rényi–Ulam game is a guessing game where some of the answers may be wrong.
He wrote 32 joint papers with Paul Erdős,[4] the most well-known of which are his papers introducing the Erdős–Rényi model of random graphs.[5] Rényi, who was addicted to coffee, invented[6] the quote: "A mathematician is a device for turning coffee into theorems.", which is generally ascribed to Erdős. The sentence was originally in German, being a wordplay on the double meaning of the word Satz (theorem or residue of coffee).
Remembrance
He is also famous for having said, "If I feel unhappy, I do mathematics to become happy. If I am happy, I do mathematics to keep happy."[7]
The Alfréd Rényi Prize, awarded by the Hungarian Academy of Science, was established in his honor.[8]
Books
- A. Rényi: Dialogues on Mathematics, Holden-Day, 1967.
- A. Rényi: A diary on information theory, Akadémiai Kiadó
- A. Rényi, Foundations of Probability, Holden-Day, Inc., San Francisco, California, 1970, xvi + 366 pp
- A. Rényi, Probability Theory. American Elsevier Publishing Company, Inc., New York, 1970, 666 pp.
References
- ^ Alfréd Rényi at the Mathematics Genealogy Project.
- ^ Kendall, David (1970), "Obituary: Alfred Renyi", Journal of Applied Probability 7 (2): 508–522, JSTOR 3211992.
- ^ Revesz, P.; Vincze, I. (1972), "Alfred Renyi, 1921-1970", The Annals of Mathematical Statistics 43 (6): i–xvi, doi:10.1214/aoms/1177690849, JSTOR 2240189.
- ^ Paul Erdős: The Master of Collaboration, Jerrold W. Grossman, March 8, 1996 Archive copy at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "On random graphs", Publ. Math. Debrecen, 1959, and "On the evolution of random graphs", Publ. Math. Inst. Hung. Acad. Sci, 1960.
- ^ Gyula O. H. Katona: Preface to Ars Mathematica, Collected writings of Alfréd Rényi, TypoTeX, Budapest, 2005, p. 8.
- ^ Quoted in Pál Turán, "The Work of Alfréd Rényi", Matematikai Lapok 21 (1970) 199 - 210.
- ^ "Rényi, Alfréd". http://www.omikk.bme.hu/archivum/angol/htm/renyi_a.htm. Retrieved 8 March 2010.